Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template and Guide
Create a snapshot of your industry, identify underlying drivers of profitability, and competence.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The model was created by Harvard professor Michael E. Porter and was initially published in his book Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors in 1980. In this model, Porter identified five forces that play a part in shaping every market and industry. According to Porter, his General Analytic Techniques known as the 5 Competitive Forces are supposed to be used to help businesses analyze their industry, understand their competitors, and strengthen their market position. The key goal of using Porter’s Five Forces is to better understand the strength and positioning of the competitors within your industry. Use it to guide your brand’s strategy and increase your competitive advantage.
When you complete your Porter's Five Forces template and guide, you:
• Identify the level of competition within your industry
• Understand how easy it is for new brands to a start-up within your industry
• Identify how many value propositions exist that compete with yours
• Identify how you stack up against your competition
• Understand the power your buyers have over your brand
• Understand the power your suppliers have over your brand
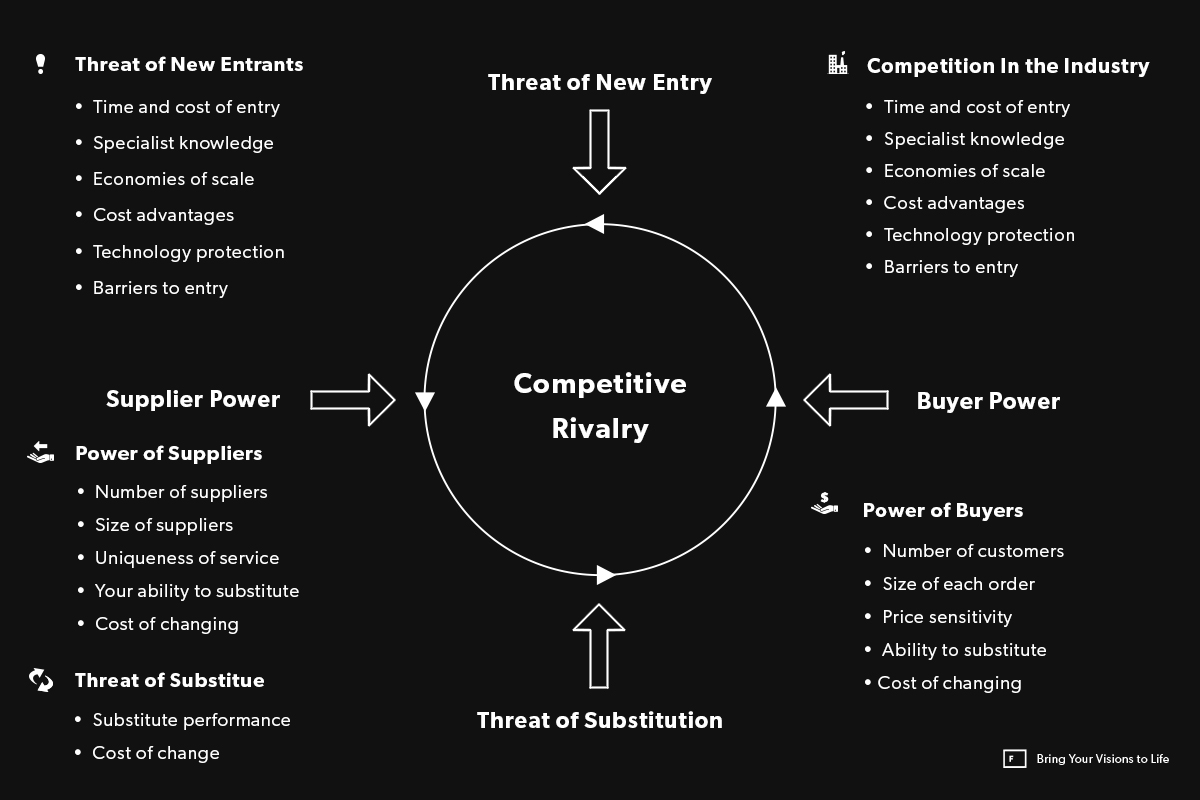 Graphical representation of Porter's Five Forces
Graphical representation of Porter's Five Forces1. Competition in the Industry
2. Threat of New Entrants
3. Threat of Substitutes
4. Power of Buyers
5. Power of Suppliers
🎉 Let's Get Started
FREE Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template and Guide
Ask Yourself
• How many competitors do you have?
• Who are your smallest competitors?
• Who are your largest competitors?
• Who is leading the industry?
• How do you compare to each identified competitor?
Remember
The larger the number of competitors, along with the number of equivalent products and services they offer, the lesser a company’s power. Suppliers and buyers seek out a company’s competition to provide a better deal or lower prices. Conversely, when competitive rivalry is soft, a company has greater power to charge higher prices and set the terms of services or products to achieve higher profits.
Ask Yourself
• How easy is it to enter your market?
• What is required (if any) to open a new business in your industry?
Consider the Following
Seven significant barriers of entry.
• Economise of scale
Cost reductions that occur when companies increase production.
• Product Differentiation
Distinguishing a product or service from others to make it more attractive to a particular target market.
• Capital Requirements
The need to invest considerable financial resources in order to compete creates a barrier to entry.
• Switching Costs
Disadvantages or expenses, along with the economic costs of switching from one alternative to another.
• Cost Disadvantages Independent of Scale
Advantages that cannot be replicated by the competition, such as proprietary technology.
• Government Policy
Controls the government has placed on the market, such as licensing requirements.
Ask Yourself
• How many substitutes exist?
• What is the cost difference between your substitutes?
• What other products/services could your customer use to replace yours?
Consider the Following
Substitutes that deserve your attention are those that:
• Are subject to trends improving their price or performance tradeoff with the industry's product.
• Are produced by industries earning high profits.
Remember
If your business has a niche, that can work to your advantage because there will be few (or no) substitutes. However, if your business isn’t as unique, you could have many threats of substitutes.
Ask Yourself
• How many buyers or customers do you have?
• Can your buyers drive your prices or terms?
• How much revenue does each buyer render?
• How sensitive are your buyers to a given price?
• How much would it cost a buyer to switch from your products and services to those of a rival?
• How loyal are your buyers?
Remember
Buyers compete with the industry by forcing down prices, bargaining for higher quality or more services, and playing competitors against each other, all at the expense of industry profitability.
Ask Yourself
• How many suppliers are in your industry?
• How unique is their product or service?
• How heavily do you rely on their products or services to run your business?
• How much would it cost you to switch suppliers?
Remember
Suppliers can exert power over you in your industry by threatening to raise prices or reduce the quality of purchased goods and services.
More suppliers equal’s higher accessibility to similar solutions, which could be advantageous for you.
Fewer suppliers mean there are more opportunities for your suppliers to drive your profitability by raising their prices.
Your Completed Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template and Guide
Your Next Steps
Now that you have an overview of your industry, it’s time to develop a comprehensive understanding of your key competitor’s positioning, value propositions, digital marketing efforts, and customer relationships. To equip yourself with the necessary information, you need to outperform your competition. Get Started Here.
The power to succeed in the palm of your hand.
✔️ Stay organized and on track.
✔️ Take control from anywhere.
✔️ Collaborate & manage with ease.
Learn More About Notion
